

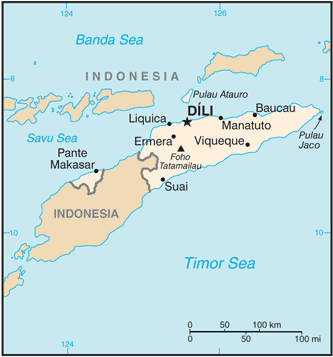
East & Southeast Asia :: TIMOR-LESTE
- Hide
Introduction :: TIMOR-LESTE
Panel - Expanded -
TThe Portuguese began to trade with the island of Timor in the early 16th century and colonized it in mid-century. Skirmishing with the Dutch in the region eventually resulted in an 1859 treaty in which Portugal ceded the western portion of the island. Imperial Japan occupied Portuguese Timor from 1942 to 1945, but Portugal resumed colonial authority after the Japanese defeat in World War II. East Timor declared itself independent from Portugal on 28 November 1975 and was invaded and occupied by Indonesian forces nine days later. It was incorporated into Indonesia in July 1976 as the province of Timor Timur (East Timor). An unsuccessful campaign of pacification followed over the next two decades, during which an estimated 100,000 to 250,000 people died. In an August 1999 UN-supervised popular referendum, an overwhelming majority of the people of Timor-Leste voted for independence from Indonesia. However, in the next three weeks, anti-independence Timorese militias - organized and supported by the Indonesian military - commenced a large-scale, scorched-earth campaign of retribution. The militias killed approximately 1,400 Timorese and forced 300,000 people into western Timor as refugees. Most of the country's infrastructure, including homes, irrigation systems, water supply systems, and schools, and nearly all of the country's electrical grid were destroyed. On 20 September 1999, Australian-led peacekeeping troops deployed to the country and brought the violence to an end. On 20 May 2002, Timor-Leste was internationally recognized as an independent state.In 2006, internal tensions threatened the new nation's security when a military strike led to violence and a breakdown of law and order. At Dili's request, an Australian-led International Stabilization Force (ISF) deployed to Timor-Leste, and the UN Security Council established the UN Integrated Mission in Timor-Leste (UNMIT), which included an authorized police presence of over 1,600 personnel. The ISF and UNMIT restored stability, allowing for presidential and parliamentary elections in 2007 in a largely peaceful atmosphere. In February 2008, a rebel group staged an unsuccessful attack against the president and prime minister. The ringleader was killed in the attack, and most of the rebels surrendered in April 2008. Since the attack, the government has enjoyed one of its longest periods of post-independence stability, including successful 2012 elections for both the parliament and president. In late 2012, the UN Security Council ended its peacekeeping mission in Timor-Leste and both the ISF and UNMIT departed the country.
- Hide
Geography :: TIMOR-LESTE
Panel - Expanded -
Southeastern Asia, northwest of Australia in the Lesser Sunda Islands at the eastern end of the Indonesian archipelago; note - Timor-Leste includes the eastern half of the island of Timor, the Oecussi (Ambeno) region on the northwest portion of the island of Timor, and the islands of Pulau Atauro and Pulau Jaco8 50 S, 125 55 ESoutheast Asiatotal: 14,874 sq kmland: 14,874 sq kmwater: 0 sq kmcountry comparison to the world: 160slightly larger than Connecticuttotal: 253 kmborder countries (1): Indonesia 253 km706 kmterritorial sea: 12 nmcontiguous zone: 24 nmexclusive fishing zone: 200 nmtropical; hot, humid; distinct rainy and dry seasonsmountainouslowest point: Timor Sea, Savu Sea, and Banda Sea 0 mhighest point: Foho Tatamailau 2,963 mgold, petroleum, natural gas, manganese, marbleagricultural land: 25.1%arable land 10.1%; permanent crops 4.9%; permanent pasture 10.1%forest: 49.1%other: 25.8% (2011 est.)346.5 sq km (2003)floods and landslides are common; earthquakes; tsunamis; tropical cycloneswidespread use of slash and burn agriculture has led to deforestation and soil erosionparty to: Biodiversity, Climate Change, Climate Change-Kyoto Protocol, Desertificationsigned, but not ratified: none of the selected agreementsTimor comes from the Malay word for "East"; the island of Timor is part of the Malay Archipelago and is the largest and easternmost of the Lesser Sunda Islands
- Hide
People and Society :: TIMOR-LESTE
Panel - Expanded -
noun: Timoreseadjective: TimoreseAustronesian (Malayo-Polynesian), Papuan, small Chinese minorityTetum (official), Portuguese (official), Indonesian, Englishnote: there are about 16 indigenous languages; Tetum, Galole, Mambae, and Kemak are spoken by a significant portion of the populationRoman Catholic 96.9%, Protestant / Evangelical 2.2%, Muslim 0.3%, other 0.6% (2005)1,231,116note: other estimates range as low as 800,000 (July 2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1600-14 years: 41.82% (male 264,636/female 250,184)15-24 years: 20.02% (male 124,937/female 121,508)25-54 years: 29.59% (male 175,569/female 188,726)55-64 years: 4.84% (male 30,584/female 29,010)65 years and over: 3.73% (male 21,948/female 24,014) (2015 est.)total dependency ratio: 92.3%youth dependency ratio: 81.5%elderly dependency ratio: 10.7%potential support ratio: 9.3% (2015 est.)total: 18.5 yearsmale: 17.9 yearsfemale: 19.1 years (2014 est.)2.42% (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 3534.16 births/1,000 population (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 306.1 deaths/1,000 population (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 158-3.86 migrant(s)/1,000 population (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 189urban population: 32.8% of total population (2015)rate of urbanization: 3.75% annual rate of change (2010-15 est.)DILI (capital) 228,000 (2014)at birth: 1.07 male(s)/female0-14 years: 1.06 male(s)/female15-24 years: 1.03 male(s)/female25-54 years: 0.93 male(s)/female55-64 years: 1.05 male(s)/female65 years and over: 0.91 male(s)/femaletotal population: 1.01 male(s)/female (2015 est.)total: 37.54 deaths/1,000 live birthsmale: 40.5 deaths/1,000 live birthsfemale: 34.39 deaths/1,000 live births (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 56total population: 67.72 yearsmale: 66.17 yearsfemale: 69.37 years (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1655.01 children born/woman (2015 est.)country comparison to the world: 1522.3% (2009/10)1.3% of GDP (2013)country comparison to the world: 1560.07 physicians/1,000 population (2011)5.9 beds/1,000 population (2010)improved:urban: 95.2% of populationrural: 60.5% of populationtotal: 71.9% of populationunimproved:urban: 4.8% of populationrural: 39.5% of populationtotal: 28.1% of population (2015 est.)improved:urban: 69% of populationrural: 26.8% of populationtotal: 40.6% of populationunimproved:urban: 31% of populationrural: 73.2% of populationtotal: 59.4% of population (2015 est.)NANANAdegree of risk: very highfood or waterborne diseases: bacterial diarrhea, hepatitis A, and typhoid fevervectorborne diseases: dengue fever and malaria (2013)1.8% (2014)country comparison to the world: 17845.3% (2010)country comparison to the world: 19.4% of GDP (2011)country comparison to the world: 7definition: age 15 and over can read and writetotal population: 67.5%male: 71.5%female: 63.4% (2015 est.)total: 12 yearsmale: 12 yearsfemale: 11 years (2010)total number: 10,510percentage: 4% (2002 est.)total: 14.8%male: 10.4%female: 22.7% (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 79
- Hide
Government :: TIMOR-LESTE
Panel - Expanded -
conventional long form: Democratic Republic of Timor-Lesteconventional short form: Timor-Lestenote: pronounced TEE-mor LESS-taylocal long form: Republika Demokratika Timor Lorosa'e [Tetum]; Republica Democratica de Timor-Leste [Portuguese]local short form: Timor Lorosa'e [Tetum]; Timor-Leste [Portuguese]former: East Timor, Portuguese Timorrepublicname: Diligeographic coordinates: 8 35 S, 125 36 Etime difference: UTC+9 (14 hours ahead of Washington, DC, during Standard Time)13 administrative districts; Aileu, Ainaro, Baucau, Bobonaro (Maliana), Cova-Lima (Suai), Dili, Ermera (Gleno), Lautem (Los Palos), Liquica, Manatuto, Manufahi (Same), Oecussi (Ambeno), Viquequenote: administrative divisions have the same names as their administrative centers (exceptions have the administrative center name following in parentheses)28 November 1975 (independence proclaimed from Portugal); note - 20 May 2002 is the official date of international recognition of Timor-Leste's independenceProclamation of Independence Day, 28 November (1975)drafted 2001, approved 22 March 2002, entered into force 20 May 2002 (2013)civil law system based on the Portuguese model; note - penal and civil law codes to replace the Indonesian codes were passed by Parliament and promulgated in 2009 and 2011, respectivelyaccepts compulsory ICJ jurisdiction with reservations; accepts ICCt jurisdiction17 years of age; universalchief of state: President Taur Matan RUAK, aka Jose Maria de VASCONCELOS (since 20 May 2012); note - the president plays a largely symbolic role but is the commander in chief of the military and is able to veto legislation, dissolve parliament, and call national electionshead of government: Prime Minister Kay Rala Xanana GUSMAO - formerly Jose Alexandre GUSMAO (since 8 August 2007); Vice Prime Minister Fernando "Lasama" de ARAUJO (since 8 August 2012)cabinet: Council of Ministers proposed by the prime minister and appointed by the presidentelections/appointments: president directly elected by absolute majority popular vote in 2 rounds if needed for a 5-year term (eligible for a second term); election last held on 17 March 2012 with a runoff on 16 April 2012; following parliamentary elections, the president appoints the leader of the majority party or majority coalition as the prime ministerelection results: Taur Matan RUAK elected president in runoff; percent of vote - Taur Matan RUAK (independent) 61.2%, Francisco GUTTERES (Frenti-Mudanca) 38.8%description: unicameral National Parliament (65 seats; members directly elected in a single nationwide constituency by proportional representation vote to serve 5-year terms)elections: elections were held on 7 July 2012 (next to be held in July 2017)election results: percent of vote by party - CNRT 36%, FRETILIN 30%, PD 10%, Frenti-Mudanca 3%, others 21%; seats by party - CNRT 30, FRETILIN 25, PD 8, Frenti-Mudanca 2highest court(s): Supreme Court of Justice (consists of the court president and NA judges)judge selection and term of office: Supreme Court president appointed by the president of the republic from among the other court judges to serve a 4-year term; other Supreme Court judges appointed - 1 by the Parliament, and the others by the Supreme Council for the Judiciary, a body presided by the Supreme Court president and includes mostly presidential and parliamentary appointees; other Supreme Court judge tenure NAsubordinate courts: Court of Appeal; district courts; magistrates' courtsnote: the UN Justice System Programme, launched in 2003 and in 2008, is helping strengthen the country's justice systemDemocratic Party or PD [Fernando "Lasama" de ARAUJO]Frenti-Mudanca [Jose Luis GUTERRES]National Congress for Timorese Reconstruction or CNRT [Kay Rala Xanana GUSMAO]Revolutionary Front of Independent Timor-Leste or FRETILIN [Mari ALKATIRI](only parties in Parliament are listed)NAACP, ADB, AOSIS, ARF, ASEAN (observer), CPLP, EITI (compliant country), FAO, G-77, IBRD, ICAO, ICCt, ICRM, IDA, IFAD, IFC, IFRCS, ILO, IMF, IMO, Interpol, IOC, IOM, IPU, ITU, MIGA, NAM, OPCW, PIF (observer), UN, UNCTAD, UNESCO, UNIDO, Union Latina, UNWTO, UPU, WCO, WHO, WMOchief of mission: Ambassador Domingos Sarmento ALVES (since 21 May 2014)chancery: 4201 Connecticut Avenue NW, Suite 504, Washington, DC 20008telephone: [1] (202) 966-3202FAX: [1] (202) 966-3205chief of mission: Ambassador (vacant); Charge d'Affaires Scott TICKNOR (since end of 2013)embassy: Avenida de Portugal, Praia dos Coqueiros, Dilimailing address: US Department of State, 8250 Dili Place, Washington, DC 20521-8250telephone: (670) 332-4684FAX: (670) 331-3206red with a black isosceles triangle (based on the hoist side) superimposed on a slightly longer yellow arrowhead that extends to the center of the flag; a white star - pointing to the upper hoist-side corner of the flag - is in the center of the black triangle; yellow denotes the colonialism in Timor-Leste's past; black represents the obscurantism that needs to be overcome; red stands for the national liberation struggle; the white star symbolizes peace and serves as a guiding lightMount Ramelau; national colors: red, yellow, black, whitename: "Patria" (Fatherland)lyrics/music: Fransisco Borja DA COSTA/Afonso DE ARAUJOnote: adopted 2002; the song was first used as an anthem when Timor-Leste declared its independence from Portugal in 1975; the lyricist, Fransisco Borja DA COSTA, was killed in the Indonesian invasion just days after independence was declared
- Hide
Economy :: TIMOR-LESTE
Panel - Expanded -
Since gaining its independence in 1999, Timor-Leste has faced great challenges in rebuilding its infrastructure, strengthening the civil administration, and generating jobs for young people entering the work force. The development of oil and gas resources in offshore waters has greatly supplemented government revenues. This technology-intensive industry, however, has done little to create jobs in part because there are no production facilities in Timor-Leste. Gas is currently piped to Australia for processing, but Timor-Leste has expressed interest in developing a domestic processing capacity. In June 2005, the National Parliament unanimously approved the creation of a Petroleum Fund to serve as a repository for all petroleum revenues and to preserve the value of Timor-Leste's petroleum wealth for future generations. The Fund held assets of $16.5 billion, as of December 2014. Oil accounts for 90% of government revenues, and the drop in the price of oil in 2014 has led to concerns about the long-term sustainability of government spending. The Ministry of Finance maintains that the Petroleum Fund is sufficient to sustain government operations for the foreseeable future. Annual government budget expenditures increased markedly between 2009 and 2012 but dropped significantly in 2013 and again in 2014. Historically, the government has failed to spend as much as its budget allowed. The government has focused significant resources on basic infrastructure, including electricity and roads. Limited experience in procurement and infrastructure building has hampered these projects. The underlying economic policy challenge the country faces remains how best to use oil-and-gas wealth to lift the non-oil economy onto a higher growth path and to reduce poverty.$6.066 billion (2014 est.)$5.693 billion (2013 est.)$5.401 billion (2012 est.)note: data are in 2014 US dollarscountry comparison to the world: 163$4.478 billionnote: non-oil GDP (2014 est.)6.6% (2014 est.)5.4% (2013 est.)7.8% (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 23$4,900 (2014 est.)$4,600 (2013 est.)$4,400 (2012 est.)note: data are in 2014 US dollarscountry comparison to the world: 155household consumption: 21.9%government consumption: 21.3%investment in fixed capital: 21.8%investment in inventories: 0%exports of goods and services: 81.9%imports of goods and services: -46.8%(2014 est.)agriculture: 5.2%industry: 72.8%services: 22.1% (2014 est.)coffee, rice, corn, cassava (manioc, tapioca), sweet potatoes, soybeans, cabbage, mangoes, bananas, vanillaprinting, soap manufacturing, handicrafts, woven cloth-15% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 198247,500 (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 167agriculture: 64%industry: 10%services: 26% (2010)11% (2013 est.)18.4% (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 15837% (2011 est.)lowest 10%: 4%highest 10%: 27% (2007)31.9 (2007 est.)38 (2002 est.)country comparison to the world: 111revenues: $400 millionexpenditures: $1.8 billion (2014 est.)8.9% of GDP (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 210-31% of GDP (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 214calendar year2.5% (2014 est.)3.3% (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 11312.8% (31 December 2014 est.)12.41% (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 61$241.4 million (31 December 2014 est.)$279.5 million (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 175$546.2 million (31 December 2014 est.)$500.2 million (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 176$-500 million (31 December 2014 est.)$-469 million (31 December 2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 185$NA$1.167 billion (2014 est.)$2.74 billion (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 38$154 million (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 202oil, coffee, sandalwood, marblenote: potential for vanilla exports$696.2 million (2013 est.)$689 million (2011 est.)country comparison to the world: 188food, gasoline, kerosene, machinerythe US dollar is used
- Hide
Energy :: TIMOR-LESTE
Panel - Expanded -
349.4 million kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 197125.3 million kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2030 kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2060 kWh (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 21079,260 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 5177,280 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 390 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 1310 bbl (1 January 2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 1990 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2011,980 bbl/day (2013 est.)country comparison to the world: 1900 bbl/day (2010 est.)country comparison to the world: 1371,264 bbl/day (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1900 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2000 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 2010 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 1940 cu m (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 139200 billion cu m (1 January 2006 est.)country comparison to the world: 46496,300 Mt (2012 est.)country comparison to the world: 181
- Hide
Communications :: TIMOR-LESTE
Panel - Expanded -
total subscriptions: 3,000subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: less than 1 (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 212total: 676,900subscriptions per 100 inhabitants: 56 (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 163general assessment: rudimentary service in urban and some rural areas, which is expanding with the entrance of new competitorsdomestic: system suffered significant damage during the violence associated with independence; limited fixed-line services; mobile-cellular services have been expanding and are now available in urban and most rural areasinternational: country code - 670; international service is available (2012)1 public TV broadcast station broadcasting nationally and 1 public radio broadcaster with stations in each of the 13 administrative districts; 1 commercial TV broadcast station, 3 commercial radio stations, and roughly 20 community radio stations (2012)at least 21 (Timor-Leste has one national public broadcaster and 20 community and church radio stations - station frequency types NA) (2007)1 (Timor-Leste has one national public broadcaster).tltotal: 12,000percent of population: 1.0% (2014 est.)country comparison to the world: 205
- Hide
Transportation :: TIMOR-LESTE
Panel - Expanded -
6 (2013)country comparison to the world: 176total: 22,438 to 3,047 m: 11,524 to 2,437 m: 1 (2013)total: 4914 to 1,523 m: 2under 914 m:2 (2013)8 (2013)total: 6,040 kmpaved: 2,600 kmunpaved: 3,440 km (2005)country comparison to the world: 150total: 1by type: passenger/cargo 1 (2010)country comparison to the world: 151major seaport(s): Dili
- Hide
Military :: TIMOR-LESTE
Panel - Expanded -
Timor-Leste Defense Force (Falintil-Forcas de Defesa de Timor-L'este, Falintil (F-FDTL)): Army, Navy (Armada) (2013)18 years of age for voluntary military service; 18-month service obligation; no conscription but, as of May 2013, introduction of conscription was under discussion (2013)males age 16-49: 305,643females age 16-49: 293,052 (2010 est.)males age 16-49: 243,120females age 16-49: 251,061 (2010 est.)male: 12,737female: 12,389 (2010 est.)2.92% of GDP (2012)2.6% of GDP (2011)2.92% of GDP (2010)country comparison to the world: 23
- Hide
Transnational Issues :: TIMOR-LESTE
Panel - Expanded -
three stretches of land borders with Timor-Leste have yet to be delimited, two of which are in the Oecussi exclave area, and no maritime or Economic Exclusion Zone boundaries have been established between the countries; maritime boundaries with Indonesia remain unresolved; in 2007, Australia and Timor-Leste signed a 50-year development zone and revenue sharing agreement in lieu of a maritime boundarycurrent situation: Timor Leste is a source, transit, and destination country for men, women, and children subjected to forced labor and sex trafficking; Timorese women and girls may be sent to India, Singapore, and Middle Eastern and other Southeast Asian countries for domestic servitude; women and girls from rural areas are also lured to the capital with promises of legitimate jobs and are then forced into prostitution or domestic servitude; Timorese family members are subject to bonded domestic or agricultural labor to repay debts; foreign migrant women are subject to sex trafficking in Timor Leste, while men and boys from Burma, Cambodia, and Thailand are forced to work on fishing boats in Timorese waters under inhumane conditionstier rating: Tier 2 Watch List – Timor Leste does not fully comply with the minimum standards for the elimination of trafficking; however, it is making significant efforts to do so; legislation that would prohibit all forms of human trafficking remains pending approval, despite being submitted to the Council of Ministers in 2012; in 2013, authorities did not investigate or prosecute any trafficking cases and did not convict any offenders; the government’s efforts to protect trafficking victims were negligible; no victims were identified or referred to NGO-provided services, although funding was allocated to an NGO shelter for this purpose; increased patrolling of territorial waters in 2013 did not lead to increased identification of trafficking victims (2014)NA
